General Overview on Establishment of a Foreign Direct Investment Company in Telecommunication Field
Business Form, Investment Value and Capital Structure
Pursuant to Article 5 paragraph (2) of Law Number 25 of 2007 on Investment as amended by Law Number 11 of 2020 on Job Creation (“Law 25/2007”), foreign direct investment must be carried out in the form of a limited liability company based on Indonesian law and domiciled in the territory of the Republic of Indonesia, unless otherwise stipulated by law. Thus, the establishment of a foreign direct investment company (“PT PMA”) is also subject to the provisions of limited liability company establishment as regulated in Law Number 40 of 2007 on Limited Liability Company as amended by Law Number 11 of 2020 on Job Creation (“Law 40/2007”).
Pursuant to Article 6 of the Investment Coordinating Board Regulation Number 6 of 2018 on Guidelines and Procedures for Licensing and Investment Facilities as amended by the Investment Coordinating Board Regulation Number 5 of 2019 (“RICB 6/2018”), a PT PMA is treated as a large businesse, unless stipulated otherwise by laws and regulations. As for what is meant by a large business, according to Article 6 paragraph (2) RICB 6/2018 a large business:
A. has a net asset of more than IDR10,000,000,000.00 (ten billion Indonesian rupiah) excluding land and buildings for a business based on the latest financial report; or
B. has annual sales proceeds of more than IDR50,000,000,000.00 (fifty billion Indonesian rupiah) based on the latest financial report.
The PT PMA, unless stipulated otherwise by the laws and regulations, must meet the investment and capital value requirements as follows1 :
A. total investment value of more than IDR10,000,000,000.00 (ten billion Indonesian rupiah), excluding land and buildings per business field of 5 (five) digits Indonesian Standard Industrial Classification (Klasifikasi Baku Lapangan Usaha Indonesia “KBLI”) per project location unless otherwise stipulated by laws and regulations;
B. the value of issued capital is the same as the paid-up capital, of at least IDR2,500,000,000.00 (two billion and five hundred million Indonesian rupiah);
C. the percentage of share ownership is calculated based on the nominal value of the shares;
D. The nominal value of shares as referred in letter c for each shareholder is at least IDR10,000,000.00 (ten million Indonesian rupiah).
The investment value mentioned above must be fulfilled by the PT PMA within a period of 1 (one) year from the date the PT PMA obtains the Business License2.
Licensing of PT PMA
With the enactment of Government Regulation Number 24 of 2018 on Electronically Integrated Business Licensing Services (“GR 24/2018”), there is business licensing reform in which there are staged licenses consisting of3:
A. Registration;
B. Granting of the Business License; and
C. Granting of the Commercial or Operational Licenses.
The business licensing reform is regulated by GR 24/2018 and applies to several business sectors, including the communications and information technology sector4. Thus, licensing for a PT PMA in the telecommunication sector is included in the scope of licensing provisions and regulated in GR 24/2018, namely through the Online Single Submission (“OSS”) licensing system.
A. Registration
Registration of a PT PMA which is engaged in the telecommunication field is conducted by accessing the OSS page. The issuance of the Business Identification Number (Nomor Induk Berusaha – “NIB”) is carried out by the OSS Institution after a PT PMA registers with complete data filling5.
B. Business License
Pursuant to the provisions of Article 21 paragraph (1) of Regulation of Investment Coordinating Board Number 1 of 2020 on Guidelines for the Implementation of Electronic Integrated Business Licensing Services (“RICB 1/2020”), the Business License is issued through the OSS system to the PT PMA. There are 4 (four) types of of Business Licenses that can be issued6:
type 1, namely Business License without Commitment fulfillment;
type 2, namely Business License with technical requirements;
type 3, namely Business License with cost requirements; and
type 4, a Business License with technical and cost requirements.
Business License type 1 is a business license that has been effective. Meanwhile, type 2 , 3 and 4 Business Licenses are Business Licenses that are not effective yet, they are conditional and become effective only after the business actor fulfills the Commitment7 of Business License8. The classification of the types of Business License could be seen in the Attachment of the Decree of the Head of Investment Coordinating Board Number 98 of 2020 on Business Licensing Issuance Standards (“DHICB 98/2020”).
C. Commercial or Operational Licenses
Furthermore, to carry out its commercial or operational activities, a PT PMA must have a Commercial or Operational License, which is a license issued by the OSS Institution for and on behalf of the minister, head of institution, governor, or regent / mayor after the Business Actor has obtained a Business License and for conducting commercial or operational activities by fulfilling the requirements and/or Commitment9. Commercial or Operational License also consists of 4 (four) sub-types such as those classified in the Business License, where the classification of the types of Commercial or Operational License as set out in the Attachment of DHICB 98/2020. With regard to Commitment fulfilling, there are provisions regarding administrative sanctions as follows10 :
1. business actors who commit violations in the form of submitting false/untrue documents or statements in submitting the fulfillment of commitment will be subject to administrative sanctions, namely license revocation and being blacklisted.
2. business actors who conduct commercialization before the fulfillment of the relevant commitment are declared fulfilled, will be subject to sanctions in the form of fines and freezing of commercial businesses activities that have been carried out.
3. business actors who have submitted fulfillment of the operation-worthy commitment but declared not fulfilled operation-worthy, in certain service areas, will be subject to sanctions of freezing of the business in the said service area.
Restrictions on Foreign Direct Investment in the Telecommunication Field
Before establishing a PT PMA, it is necessary to pay attention to the provisions regarding a list of closed business fields and open business fields with conditions for foreign investment.
Closed business fields are certain business fields that are prohibited for foreign investments11. While open business fields with conditions are certain business fields that can be undertaken for investment activities with conditions, namely reserved for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises and Cooperatives (“UMKMK”), Partnerships, capital ownership, certain locations, special licenses, and investment from Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries12. The following table is a list of restrictions on conducting business activities for foreign parties (known as the Negative Investment List) in the telecommunications field13 :
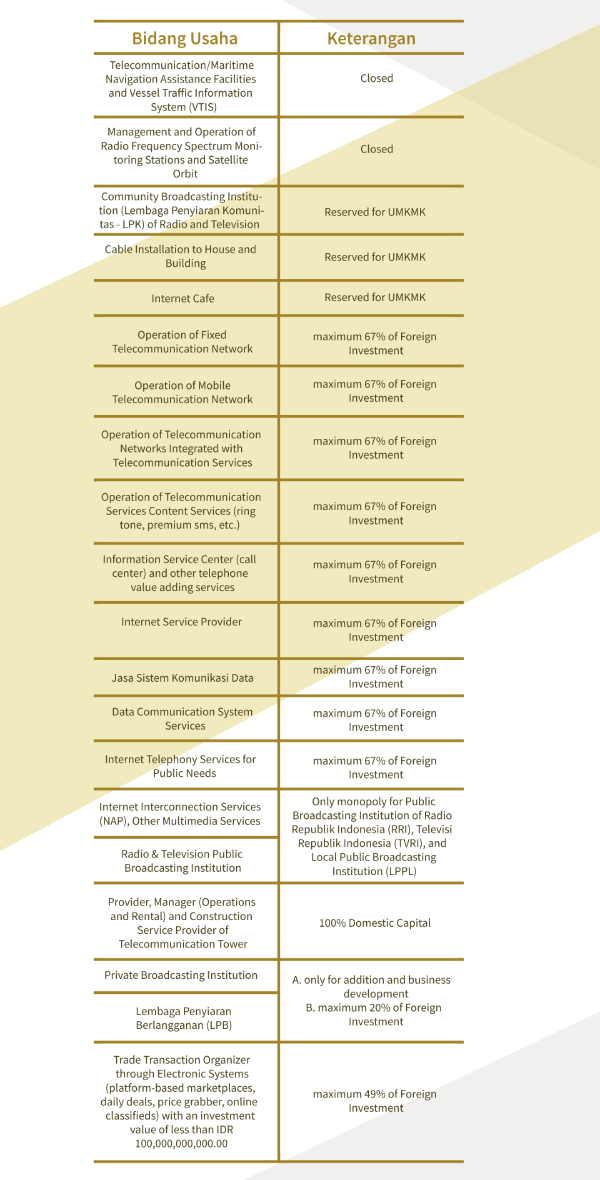
With the enactment of Law Number 11 of 2020 on Job Creation, there is a change in the concept of Negative Investment List to become the Priority Investment List, where all business fields are open for investment activities, except for business fields that are declared closed for investment or activities
that can only be carried out by the Central Government14. However, at the time of writing this Arti- cle, there is still no Presidential Regulation providing further provisions regarding the Priority Invest- ment List as mandated by Article 12 paragraph (3) of Law 25/2007. (HAL/TWK)
1. Article 6 paragraph (3) of RICB 6/2018 in conjunction with Article 6 paragraph (2) letter a of RICB 1/2020
2. Article 6 paragraph (5) of RICB 6/2018
3. Article 84 paragraph (4) of GR 24/2018
4. Article 85 of GR 24/2018
5. Article 11 paragraph (1) of RICB 1/2020
6. Article 21 paragraph (2) of RICB 1/2020
7. Pursuant to Article 1 number 14 of RICB 1/2020, Commitment is a statement by a Business Actor to fulfill the requirements for a Busi- ness License and/or Commercial or Operational License.
8. Article 23 paragraph (1) of RICB 1/2020
9. Article 1 number 17 of RICB 1/2020
10. Article 94 of Regulation of the Minister of Communication and Informatics Number 7 of 2018 on Electronic Integrated Business Licensing Services in the Communication and Informatics Sector as amended by Regulation of the Minister of Communication and Informatics Number 7 of 2019
11. Article 1 number 3 of Presidential Regulation Number 44 of 2016 on List of Closed Business Fields and Business Fields Opened with Requirements in the Field of Investment (“PR 44/2016”)
12. Article 1 number 4 of PR 44/2016
13. Attachment I-III of PR 44/2016
14. Article 12 paragraph (1) of Law 25/2007


